
View live population, charts & trends: Population of New Zealand
The median age in New Zealand is 37.5 years (2024).
A Total Fertility Rate (TFR) of 2.1 represents the Replacement-Level Fertility: the average number of children per woman needed for each generation to exactly replace itself without needing international immigration. A value below 2.1 will cause the native population to decline
See also: Countries in the world ranked by Life Expectancy
The 2024 population density in New Zealand is 20 people per Km2 (51 people per mi2), calculated on a total land area of 263,310 Km2 (101,665 sq. miles).
| # | CITY NAME | POPULATION |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Auckland | 417,910 |
| 2 | Wellington | 381,900 |
| 3 | Christchurch | 363,926 |
| 4 | Manukau City | 362,000 |
| 5 | North Shore | 207,865 |
A Population pyramid (also called "Age-Sex Pyramid") is a graphical representation of the age and sex of a population.
Types:
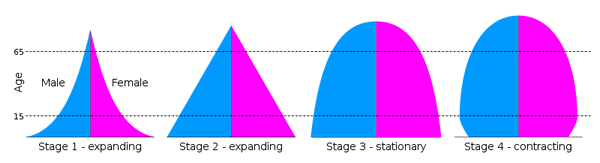
Stages:
There are three types of age dependency ratio: Youth, Elderly, and Total. All three ratios are commonly multiplied by 100.
Youth Dependency Ratio
Definition: population ages 0-15 divided by the population ages 16-64.
Formula: ([Population ages 0-15] ÷ [Population ages 16-64]) × 100
Elderly dependency ratio
Definition: population ages 65-plus divided by the population ages 16-64.
Formula: ([Population ages 65-plus] ÷ [Population ages 16-64]) × 100
Total dependency ratio
Definition: sum of the youth and old-age ratios.
Formula: (([Population ages 0-15] + [Population ages 65-plus]) ÷ [Population ages 16-64]) × 100
NOTE: Dependency Ratio does not take into account labor force participation rates by age group. Some portion of the population counted as "working age" may actually be unemployed or not in the labor force whereas some portion of the "dependent" population may be employed and not necessarily economically dependent.